This chapter focuses on the topic of viral geometry problems and the various approaches that can be used to tackle them. These problems can be quite complex and challenging, requiring a deep understanding of geometric concepts and creative problem-solving skills.
Rectangle Problems
Que 1: In the given figure ABCD is a rectangle then find the length of AE.
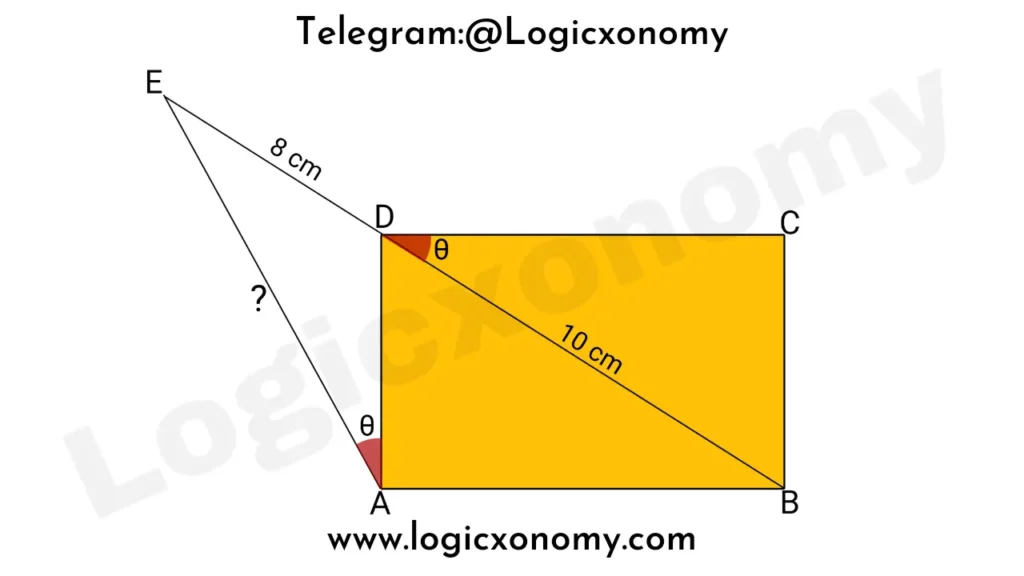
Solution: Extend the side CD to F
Theorem 1: Since ∠FDA=90°, we can draw a circumcircle of the △FDA. Here AF is the diameter of the Circle.
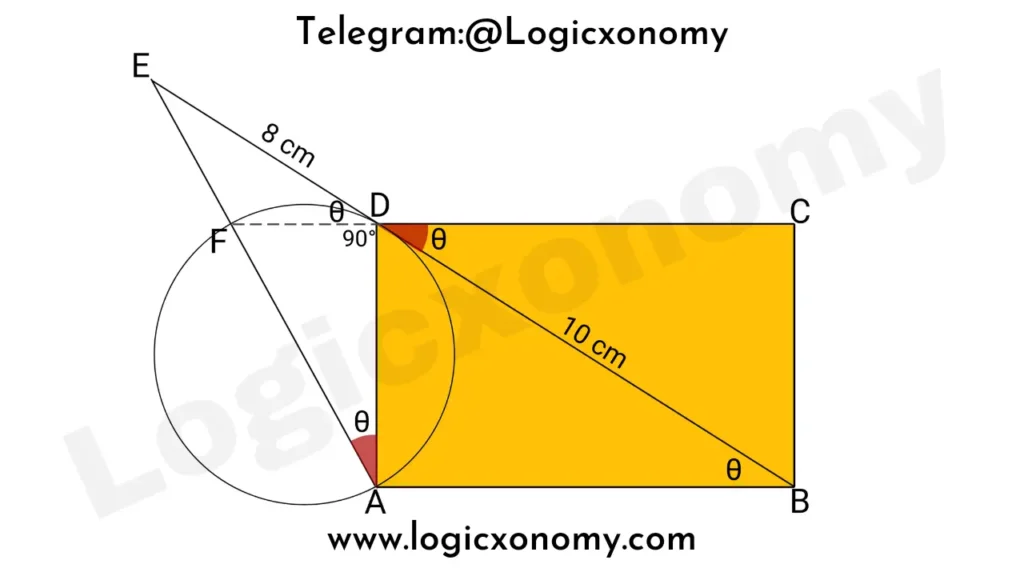
Theorem 2: Since FD is the tangent and EA is the secant of the circle.
So, ED2=EF×EA …….(i)
∠EDF=∠CDB (Vertically Opposite Angles)
∠CDB=∠ABD (Alternate angles)
△EDF~△EBA (Similar triangles)
\frac{EF}{AE}= \frac{ED}{BE}= \frac{8}{18}= \frac{4}{9}.
Let, EF=4k and AE=9k, Put these values in equation (i)
82=4k×9k
k=4/3
So, AE=9k= 12 cm
The Altitudes of a Triangle
If the side lengths of △PQR are 13, 14, and 15 cm then find the value of \frac{1}{h_1}+\frac{1}{h_2}+\frac{1}{h_3}?
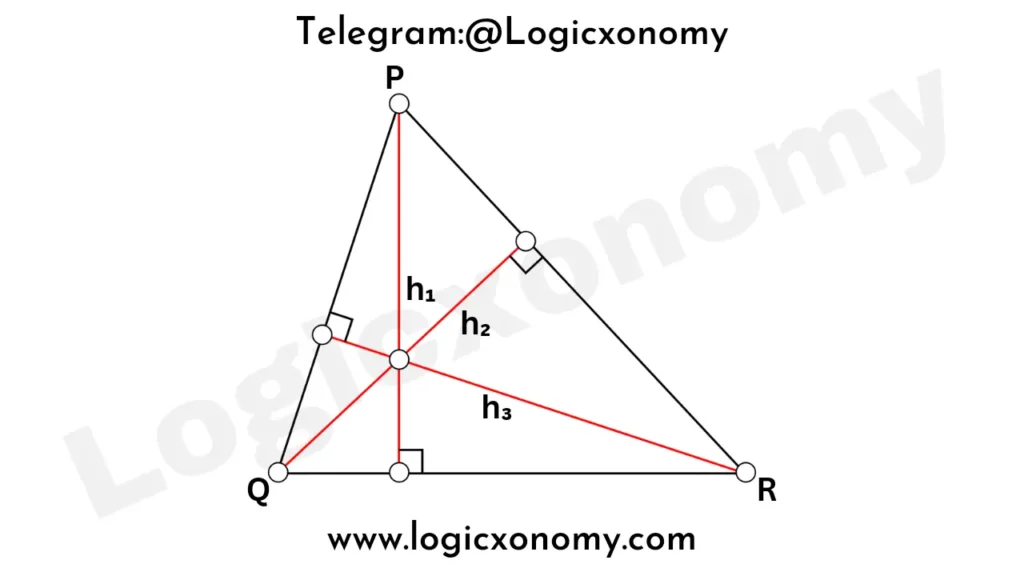
Solution: Let, the length of QR=a, PR=b, and PQ=c
Area of the triangle (△)= 1/2×Base×Height
\triangle=\frac{1}{2}\times a\times h_1.
\frac{1}{h_1}=\frac{a}{2\triangle} ………(i)
\frac{1}{h_1}+\frac{1}{h_2}+\frac{1}{h_3}=\frac{1}{2\triangle}(a+b+c)=\frac{s}{\triangle}=\frac{1}{r} ………(ii)
Here, s is the semi-perimeter (Viral Geometry Problems)
2s=a+b+c
r is the inradius of the triangle
s=(13+14+15)/2=21
\triangle=\sqrt{s\times (s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}.
\triangle=\sqrt{21\times (21-13)(21-14)(21-15)}.
\triangle=\sqrt{21\times 8\times 7\times 6}.
\triangle=84 cm2
\frac{1}{h_1}+\frac{1}{h_2}+\frac{1}{h_3}=\frac{21}{84}=0.25
Carnot’s Theorem
Carnot’s Theorem states that the sum of the signed lengths of the pedal lines from the circumcenter O to the sides of a triangle ABC is equal to the sum of the Inradius and Circumradius of the triangle.
OX+OY+OZ=R+r
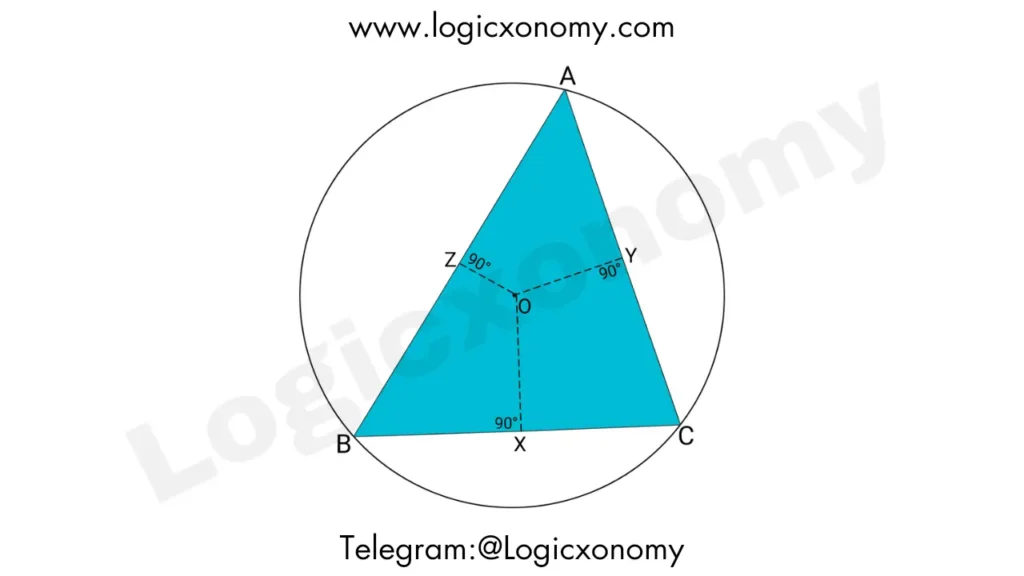
Quadrilaterals AZOY, BZOX, and CXOY are Cyclic Quadrilaterals because pair of opposite angles is equal to 180°
In AZOY⇒ OZ.AY+OY.AZ=AO.ZY (Ptolemy’s Theorem)
OX, OY, and OZ are the perpendicular bisectors of the sides of the triangle because AB, BC, and CA are the chords of the circle and O is its center.
Let BC=a, CA=b, and AB=c
AZ=a/2 and AY=b/2
AO= R (length of circumradius of the triangle)
Since Z and Y are the mid-points of the sides so ZY=BC/2=a/2
OZ.AY+OY.AZ=AO.ZY
OZ.b/2+OY.c/2=R.a/2
OZ.b+OY.c=R.a ………….(i)
Similarly, in BZOX⇒ OZ.a+OX.c=R.b ……….(ii)
Similarly, in CXOY⇒ OX.b+OY.a=R.c ……….(iii)
Add all equations:
OX.(b+c)+OY.(a+c)+OZ.(a+b)=R.(a+b+c)
Put, 2s=a+b+c
Here ‘s’ is the semi-perimeter of the triangle
OX.(2s-a)+OY.(2s-b)+OZ.(2s-c)=R.2s
2s.(OX+OY+OZ)-(a.OX+b.OY+c.OZ)=R.2s ……..(iv)
Here, ar(△BOC)+ar(△COA)+ar(△AOB)=ar(△ABC)
½.BC.OX+½.AC.OY+½.AB.OZ=△
a.OX+b.OY+c.OZ=2△
Put this value in equation (iv):
2s.(OX+OY+OZ)-2△=R.2s
OX+OY+OZ=R+△/s
OX+OY+OZ=R+r
Here ‘r’ is the inradius of the triangle.
Que: If a=13 cm, b=14 cm, and c=15 cm then find the value of OX+OY+OZ.
Solution: s=21
△2=s.(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)
△=84 cm2
R=\frac{abc}{4\triangle}=\frac{13\times 14\times 15}{4\times 84}=8.125.
r=\frac{\triangle}{s}=\frac{84}{21}=4.
OX+OY+OZ=R+r= 12.125 cm
Shaded Area inside a triangle
Que: Find the ratio of the areas of △DEF and △ABC.
Solution: ar(△DAF)= ½×AD×AF×Sin(A)
ar(△ABC)=△=½×AB×AC×Sin(A)
ar(△DAF): ar(△ABC)= AD×AF: AB×AC= (AD/AB)×(AF/AC): 1
ar(△DAF)= (AD/AB)×(AF/AC)×△
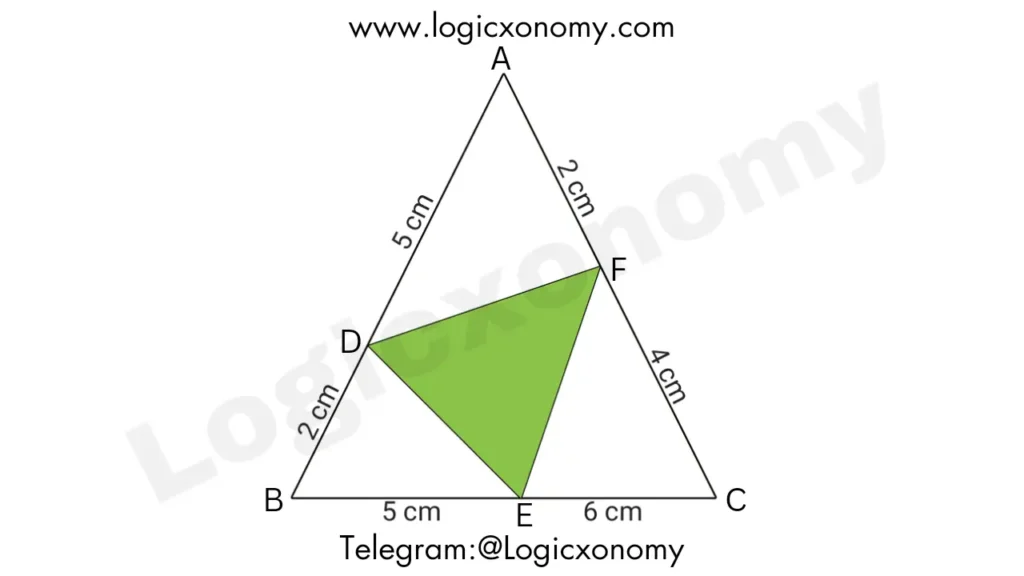
ar(△DAF)= (5/7)×(2/6)×△=(5/7)×(1/3)×△
ar(△DBE)= (2/7)×(5/11)×△
ar(△ECF)= (6/11)×(4/6)×△=(6/11)×(2/3)×△
ar(△DEF)= △-△×[(5/7)×(1/3)+(2/7)×(5/11)+(6/11)×(2/3)]
= (62/231)×△
ar(△DEF): ar(△ABC)= 62: 231
Conversion of quadrilateral to triangle
Que: Find the area of quadrilateral ABCD, If ∠BAC=35°, ∠ACD=10°, ∠ADC=45°, and side AB=10 cm.
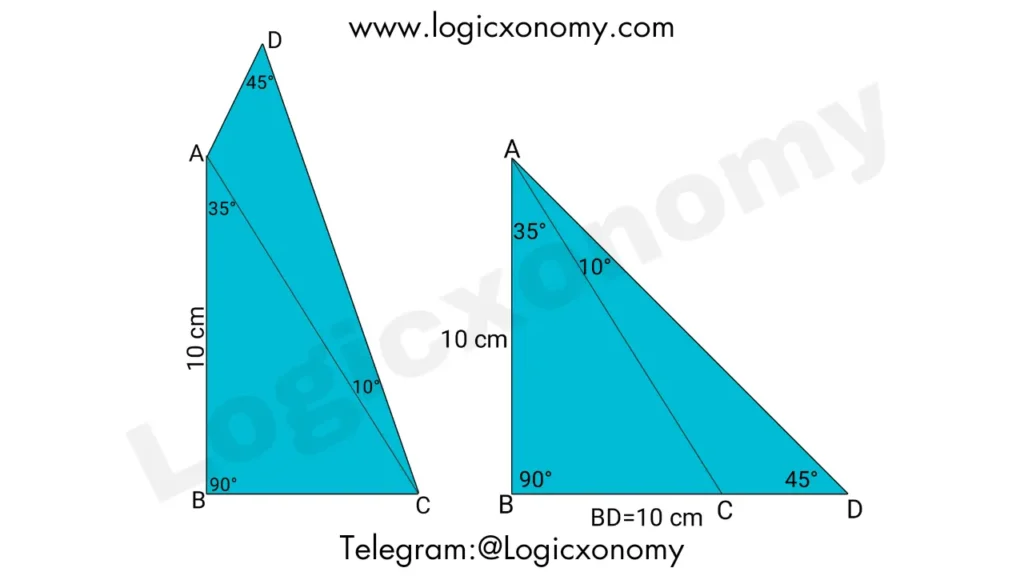
Solution: Flip the triangle CAD vertically and arrange it as shown in the picture
Now △ABD is an isosceles triangle because its two angles are 45°.
AB=BD=10 cm
Area of the △ABD=½×Base×Height
=½×10×10
=50 cm2
Miscellaneous
Que 6: In the parallelogram ABCD, where IJ is parallel to AD, and ED and HF are perpendicular to DC, what is the ratio of the areas of quadrilateral AGJI to triangle HFC?
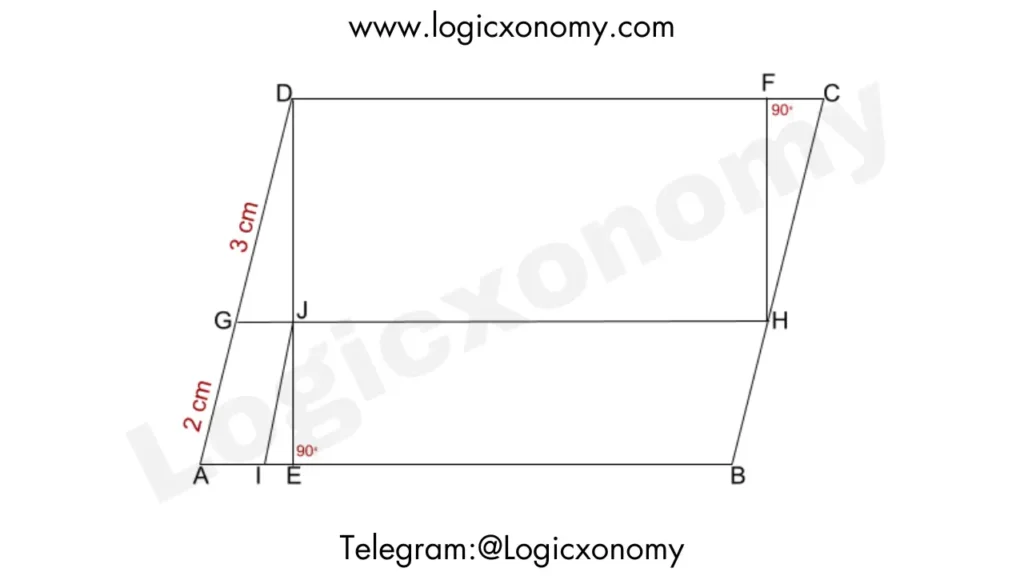
Solution: In △ADE, GJ∥AE
So, ar(△GJD): ar(△AED)=GD2: AD2=9:25
ar(AEJG)= 25-9= 16 unit …………..(i)
△IEJ ~△GJD (Similar Triangles)
ar(△IEJ): ar(△GJD)=IJ2:GD2=4:9
ar(△IEJ)=4 unit ………(ii)
ar(△HFC)=ar(△GJD)=9 unit
ar(AGJI): ar(△HFC)=16-4: 9=12:9= 4:3
Que 7: In the rectangle ABCD, the diagonal AC is extended to point E such that CE measures 5 cm. If the lengths of sides AB and BC are 8 cm and 6 cm respectively, what is the length of DE?
Solution:
Length of diagonal AC=10 cm
In △AED, AD∥FC
EF:FD=EC: CA=1:2
Let, EF=k and FD=2k ……..(i)
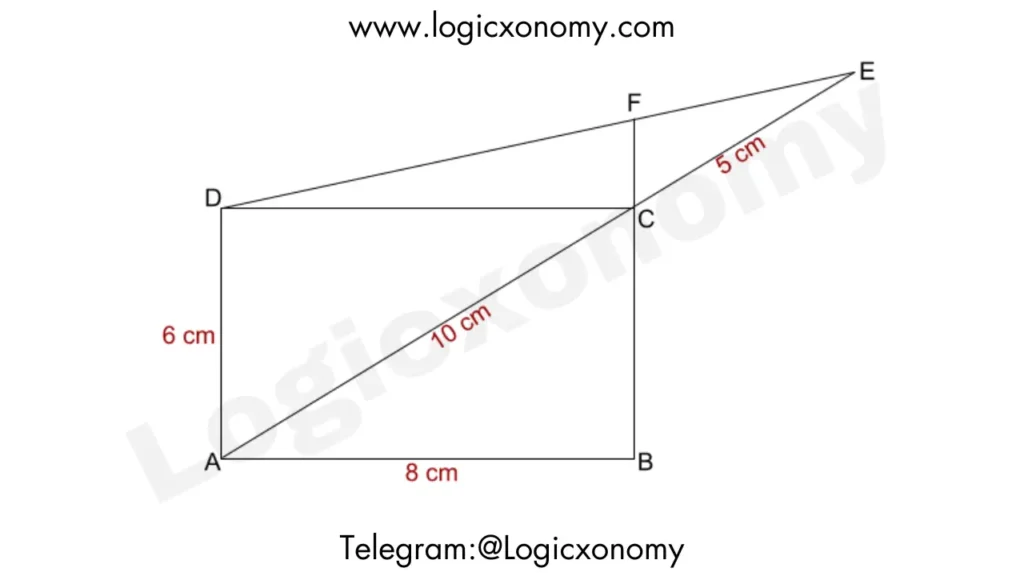
FC:AD=EC:EA=5:15
FC:6=1:3
FC=2 cm
In the right △DCF, DF2=DC2+FC2
4k2=64+4=68
2k=2√17
k=√17
DE=3k= 3√17 cm