Menelaus Theorem is named for Menelaus of Alexandria, a Greek mathematician, and astronomer. The internal and external division concepts of the triangle with proof are given below:
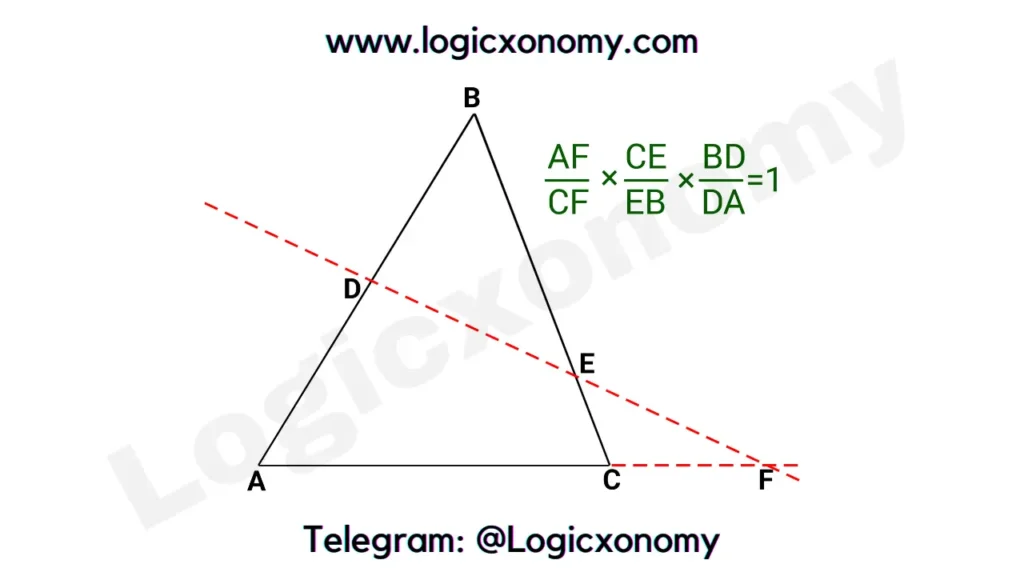
In the given figure, a transversal line (Red) is drawn, cutting sides of the ∆ABC at D, E & F.
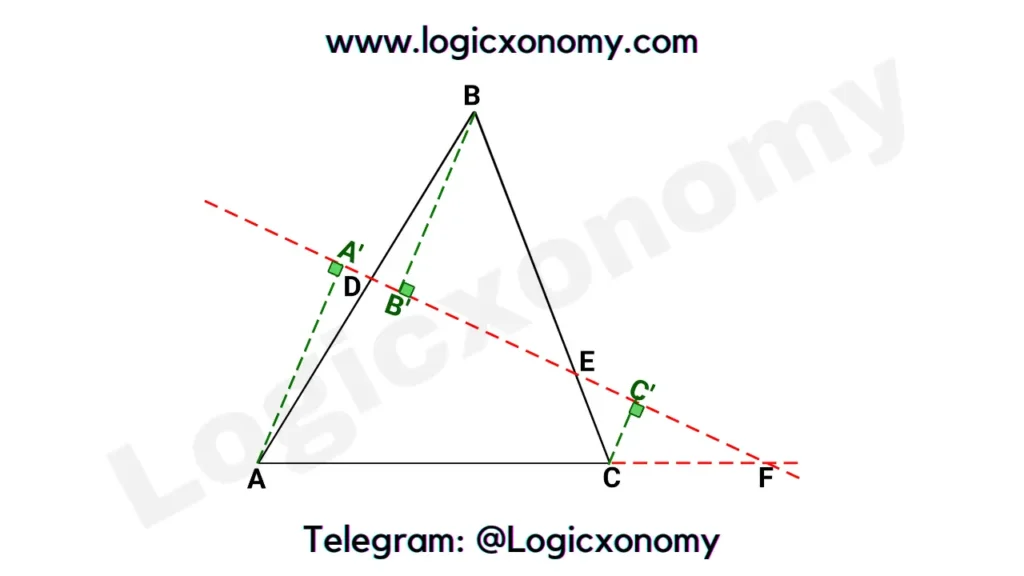
Construct perpendiculars AA’, BB’, and CC’.
Now, Since ∆AA’D ~ ∆BB’D (Similar)
BD/DA=BB’/AA’
Since ∆BB’E ~ ∆CC’E
CE/EB=CC’/BB’
Since ∆AA’F ~ ∆CC’F
AF/CF=AA’/CC’
(AF/CF)×(CE/EB)×(BD/DA)=(AA’/CC’)×(CC’/BB’)×(BB’/AA’)
(AF/CF)×(CE/EB)×(BD/DA)=1 …………….(i)
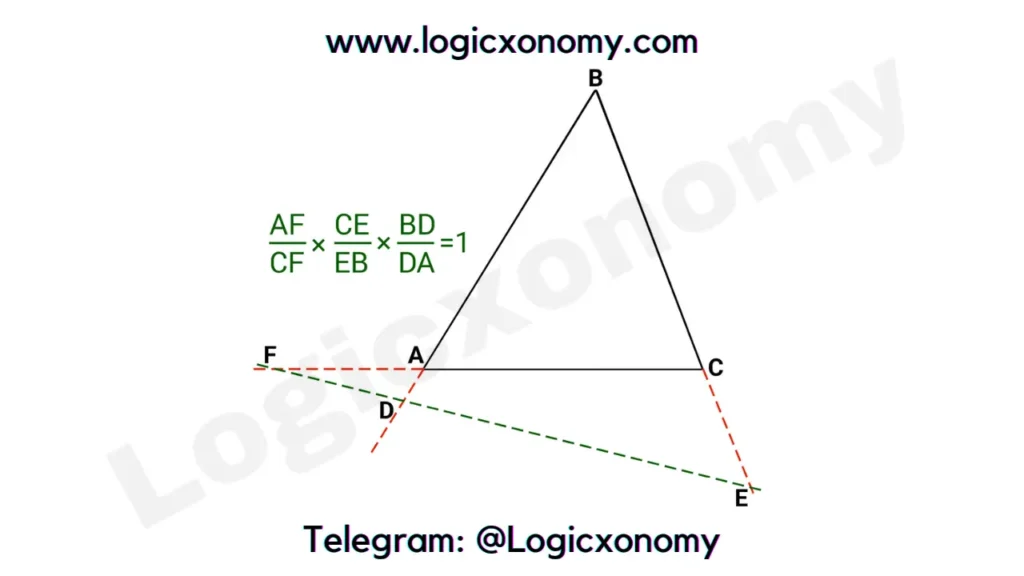
Equality still holds even when the Red Line does not intersect the triangle at all.
Construct perpendiculars AA’, BB’, and CC’.
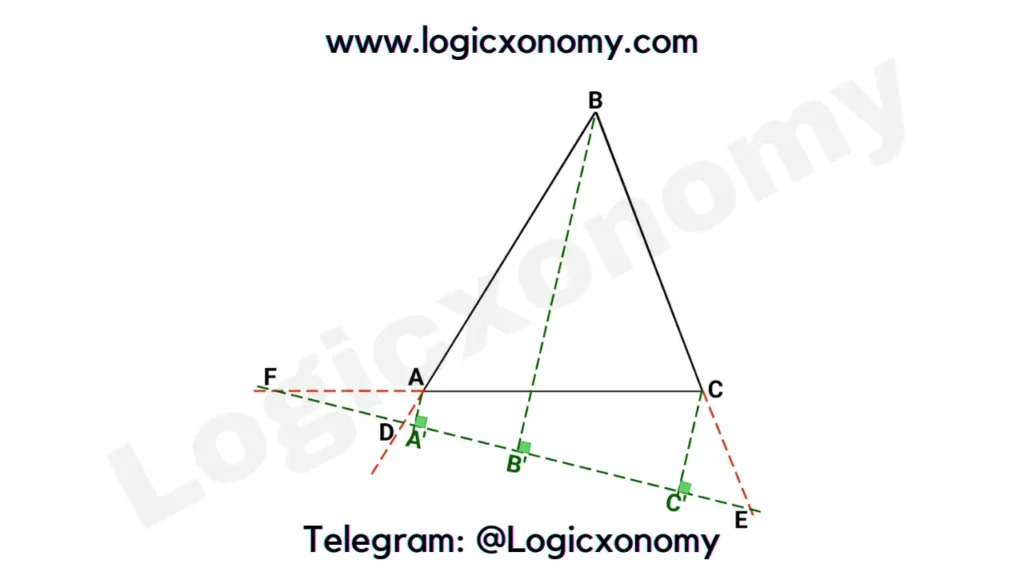
Now, Since ∆AA’F ~ ∆CC’F (Similar)
AF/CF=AA’/CC’
Since ∆BB’D ~ ∆AA’D
BD/AD=BB’/AA’
Since ∆BB’E ~ ∆CC’E
CE/EB=CC’/BB’
(AF/CF)×(CE/EB)×(BD/DA)=(AA’/CC’)×(CC’/BB’)×(BB’/AA’)
(AF/CF)×(CE/EB)×(BD/DA)=1 …………….(ii)

Application of Menelaus Theorem
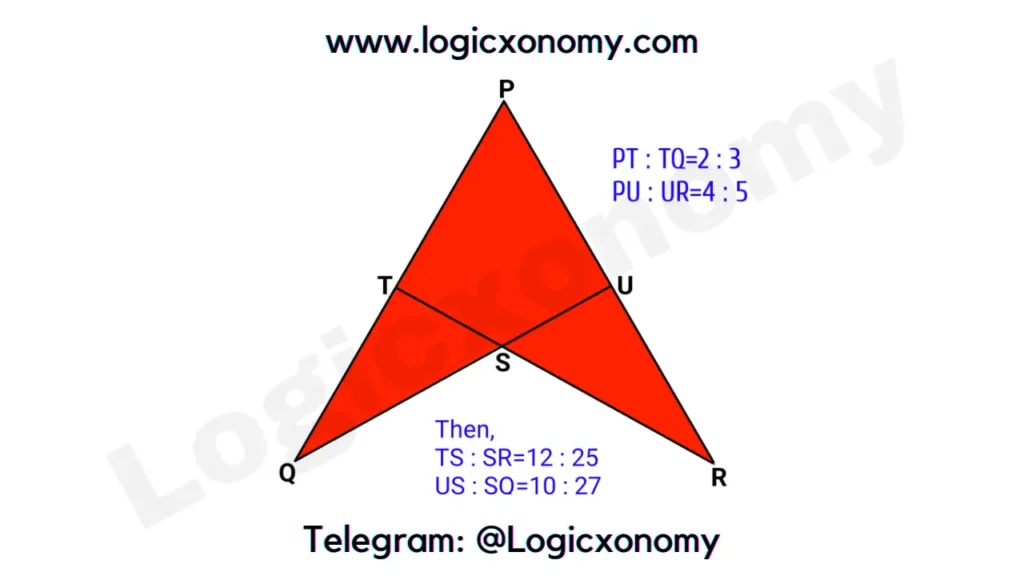
In the given figure, if PT: TU=2 : 3 and PU : UR=4: 5 then find TS: SR and US: SQ?
Step :1
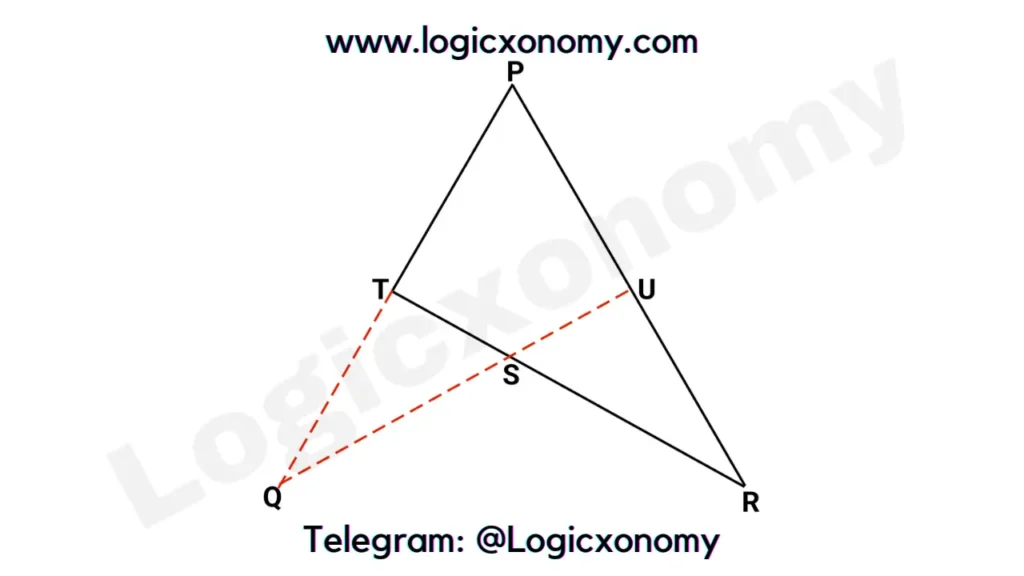
(PQ/TQ)×(TS/SR)×(RU/UP)=1
(5/3)×(TS/SR)×(5/4)=1
TS: SR=12: 25 ……………..(i)
Step:2
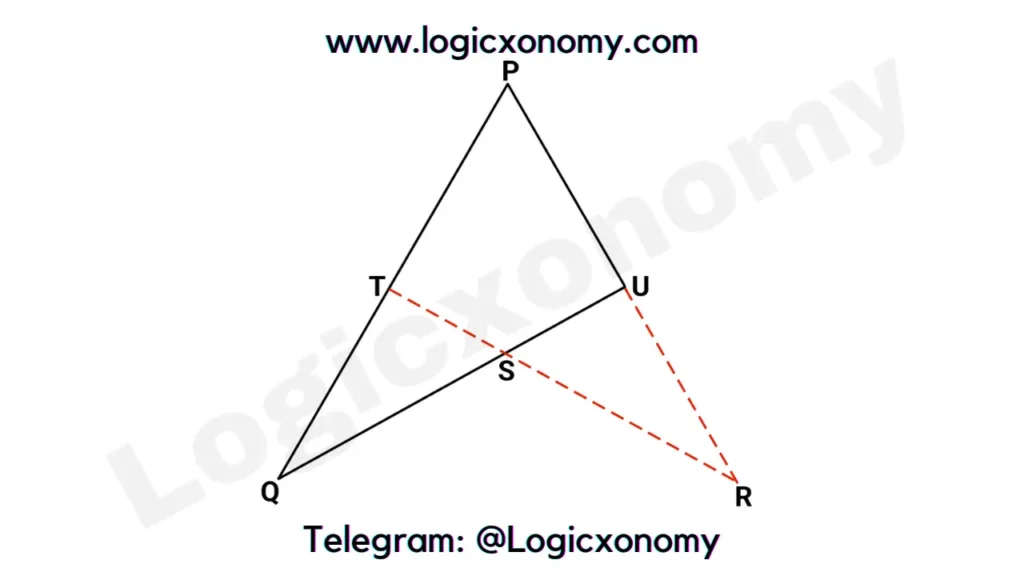
(PR/UR)×(US/SQ)×(QT/TP)=1
(9/5)×(US/SQ)×(3/2)=1
US : SQ=10 : 27 ……………..(ii)
Inradius and Circumradius of the Triangle: Click Here

